| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- Tree
- sorting
- bit manipulation
- greedy
- Number Theory
- 코테
- 구현
- Binary Search
- hash table
- array
- simulation
- Matrix
- 자바
- Stack
- Binary Tree
- dynamic programming
- implement
- 코딩테스트
- Counting
- string
- geometry
- java
- Data Structure
- Class
- Math
- 파이썬
- Method
- two pointers
- SQL
- database
- Today
- Total
코린이의 소소한 공부노트
Collections 클래스 본문

[코딩에 유용한 static 메서드를 제공하는 클래스]
1. Objects: 객체 다루기
2. Arrays: 배열 다루기
3. Collections: 컬렉션 다루기
[기능으로 분류한 Collections의 메서드]
1. 컬렉션 채우기, 복사, 정렬, 검색 – fill(), copy(), sort(), binarySearch() 등
2. 컬렉션의 동기화가 필요할 때 – synchronizedXXX()
static Collection synchronizedCollection(Collection c)
static List synchronizedList(List list)
static Set synchronizedSet(Set s)
static Map synchronizedMap(Map m)
static SortedSet synchronizedSortedSet(SortedSet s)
static SortedMap synchronizedSortedMap(SortedMap m)
// 사용법
List syncList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList());
// 동기화된 list 사용은 Vector 클래스 사용과 거의 비슷하다.3. 변경불가(readOnly) 컬렉션 만들기 – unmodifiableXXX()
static Collection unmodifiableCollection(Collection c)
static List unmodifiableList(List lilst)
static Set unmodifiableSet(Set s)
static Map unmodifiableMap(Map m)
static NavigableSet unmodifiableNavigableSet(NavigableSet s)
static SortedSet unmodifiableSortedSet(SortedSet s)
static NavigableMap unmodifiableNavigableMap(NavigableMap m)
static SortedMap unmodifiableSortedMap(SortedMap m)4. 싱글톤 컬렉션(객체 1개만 저장하는 컬렉션) 만들기 – singletonXXX()
static List singletonList(Object o)
static Set singleton(Object o) // singletonSet이 아님
static Map singletonMap(Object key, Object value)5. 한 종류의 객체만 저장하는 컬렉션 만들기 – checkedXXX()
static Collection checkedCollection(Collection c, Class type)
static List checkedList(List list, Class type)
static Set checkedSet(Set s, Class type)
static Map checkedMap(Map m, Class keyType, Class valueType)
static Queue checkedQueue(Queue queue, Class type)
static NavigableSet checkedNavigableSet(NavigableSet s, Class type)
static SortedSet checkedSortedSet(SortedSet s, Class type)
static NavigableMap checkedNavigableMap(NavigableMap m, Class keyType, Class valueType)
static SortedMap checkedSortedMap(SortedMap m, Class keyType, Class valueType)
// 사용법
List list = new ArrayList();
List checkedList = checkedList(list, String.class); // String만 저장 가능
checkedList.add(“abc”); // OK
checkedList.add(new Integer(3)); // 에러. ClassCastException 발생
[Collections의 메서드 코드 예시]
List list = new ArrayList(); // 변경 가능
System.out.println(list); // []
addAll(list, 1,2,3,4,5); // java.util.Collections 클래스에 있는 메서드
System.out.println(list); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
rotate(list, 2); // 오른쪽으로 두 칸 이동
System.out.println(list); // [4, 5, 1, 2, 3]
swap(list, 0, 2); // 0번째와 2번째 자리 바꾼
System.out.println(list); // [1, 5, 4, 2, 3]
shuffle(list); // 저장 위치를 임의로 변경
System.out.println(list); // [1, 3, 2, 5, 4]
sort(list, reverseOrder()); // 역순으로 정렬, reverse(list);와 같은 결과
System.out.println(list); // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
sort(list); // 정렬
System.out.println(list); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
int idx = binarySearch(list, 3); // 3이 저장된 위치, binarySearch() 호출 전 정렬 필수
System.out.println("index of 3 = " + idx); // index of 3 = 2
System.out.println("max= "+max(list)); // max= 5
System.out.println("min= "+min(list)); // min= 1
System.out.println("min= "+max(list, reverseOrder())); // min= 1
fill(list, 9); // list를 9로 채움
System.out.println("list= "+list); // list= [9, 9, 9, 9, 9]
// list와 크기가 같은 새 list를 만들고 2로 채운다. 이 새 리스트는 변경불가
List newList = nCopies(list.size(), 2);
System.out.println("newList="+newList); // newList= [2, 2, 2, 2, 2]
// disjoint(): 공통요소가 없다면 true
System.out.println(disjoint(list, newList)); // true
copy(list, newList); // newList의 내용을 list에 복사
System.out.println("newList= "+newList); // newList= [2, 2, 2, 2, 2]
System.out.println("list= "+list); // list= [2, 2, 2, 2, 2]
replaceAll(list, 2, 1); // list의 2를 모두 1로 변경
System.out.println("list= "+list); // list= [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
Enumeration e = enumeration(list); // iterator()와 같은 메서드
ArrayList list2 = list(e);
System.out.println("list2= "+list2); // list2= [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
[컬렉션 클래스 요약 정리]
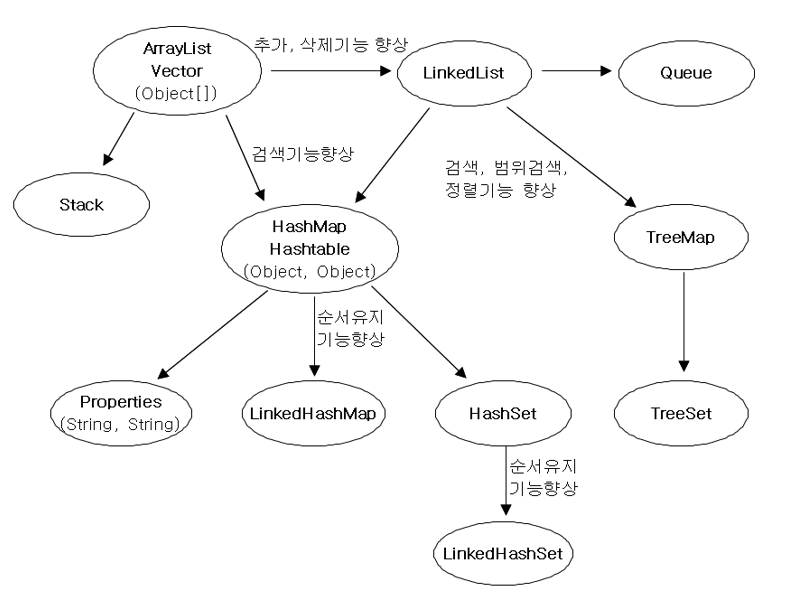
- ArrayList, Vector: 배열 기반 클래스 -> Stack: LIFO
- 배열의 단점: 추가, 삭제 불리 -> LinkedList: 연결 기반 -> Queue: FIFO
- 배열과 링크드 리스트를 결합해 검색 기능 향상 -> HashMap, Hashtable
- 링크드 리스트의 검색, 정렬 기능 향상 -> TreeMap
- HashMap/TreeMap의 key 부분만 살린 형태 -> HashSet/TreeSet
- HashMap의 key와 value를 String으로 저장한 형태 -> Properties: 파일 IO가 용이함
- HashMap/HashSet의 순서유지 기능 향상 -> LinkedHashMap/LinkHashSet
[쿠키글] Properties 클래스
1. 내부적으로 Hashtable을 사용하며, key와 value를 (String, String)으로 저장한다.
2. 주로 애플리케이션의 환경설정에 관련된 속성을 저장하는 데 사용되며 파일로부터 편리하게 값을 읽고 쓸 수 있는 메서드를 제공한다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 지네릭스와 다형성 (0) | 2022.11.09 |
|---|---|
| 지네릭스 (0) | 2022.11.09 |
| HashMap, Hashtable 클래스 (0) | 2022.11.08 |
| TreeSet 클래스 (0) | 2022.11.07 |
| HashSet 클래스 (0) | 2022.11.07 |




